Vitiligo Treatment

Introduction
- What is Vitiligo?
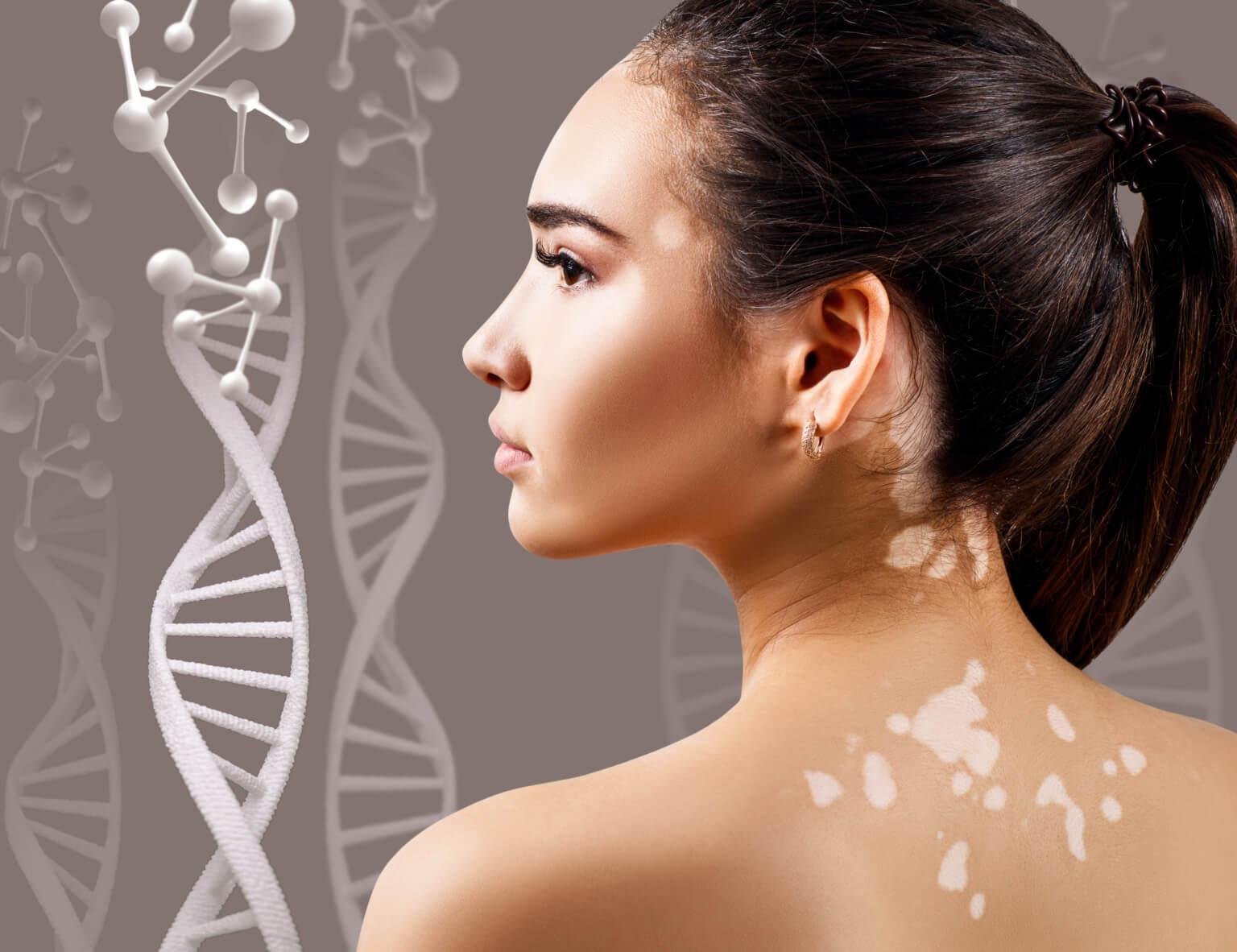
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition that causes white patches to appear on different areas of the body. It occurs when pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin stop functioning. This happens due to the destruction or malfunction of melanocytes, the skin cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. As a result, affected areas appear white or pink.
Vitiligo can manifest anywhere on the body but is more commonly found in certain areas, including:
- Around the eyes, nostrils, and belly button
- On the elbows and genitals
- Inside the mouth
- Areas with skin folds, such as the knees and elbows
Additionally, because melanocytes also pigment hair, individuals with vitiligo may experience premature graying of hair or a loss of color on their lips.
Vitiligo is not contagious and can affect people of all ages and ethnicities.
- Impact of Vitiligo:
While not medically harmful, vitiligo can significantly impact a person’s emotional and social well-being. The visible patches can cause feelings of self-consciousness, anxiety, and social isolation.

Research Article on Vitiligo
Department of Dermatology, Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Nerul, Navi Mumbai, India
Vitiligo has important clinical and social consequences particularly in the pigmented skin. The present study was conducted to assess the differences in clinicoepidemiological presentation of vitiligo in males and females and to understand the factors associated with spread of vitiligo in them. Methods. This is a cross‐sectional analysis of secondary clinical data of 168 vitiligo patients at a tertiary medical centre at Navi Mumbai. We used logistic regression models to estimate the association between gender and clinical characteristics of vitiligo and to evaluate the factors associated with spread of vitiligo. Results. There were no significant differences between the mean ages of males and females; however, males reported a longer duration of disease (6.9 (10.4) years) compared with females (4.9 (7.4) years). Males were significantly more likely to report a family history of vitiligo compared with females

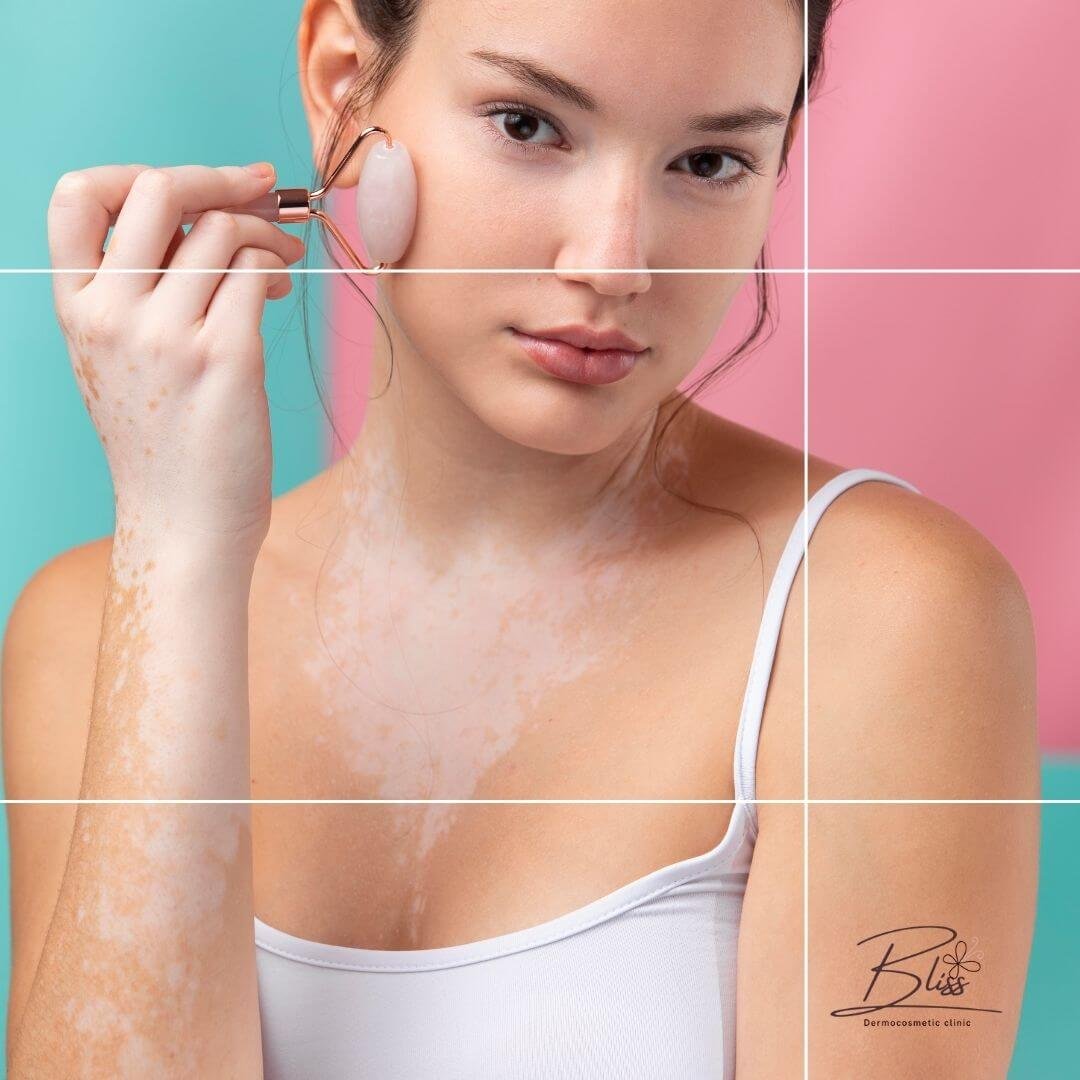
Who Can Get Vitiligo?
Vitiligo can affect anyone, regardless of age, skin color, or ethnic background. However, it tends to be more noticeable in individuals with darker skin tones. Those with lighter skin may not immediately realize they have vitiligo
- The condition is more prevalent among people with a family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune diseases. Although vitiligo can begin at any age, approximately 95% of those affected develop the condition before reaching 40.

Types of vitiligo
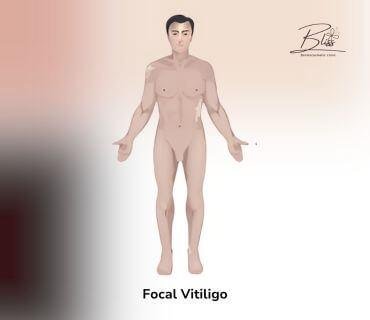
Focal Vitiligo
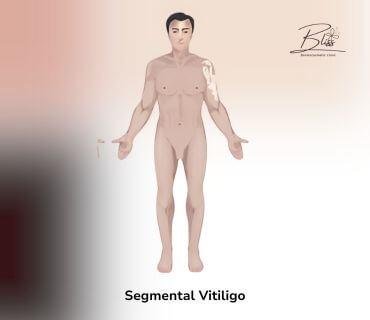
Segmental Vitiligo
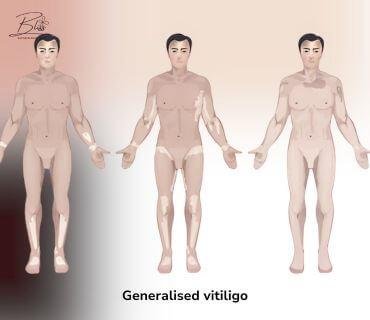
Generalised Vitiligo
Focal Vitiligo:
- Few vitiligo spots in one specific area
- Few vitiligo spots in one specific area
Segmental Vitiligo:
- Patches usually on one side of the body only
- Most unusual form of vitiligo
Generalised Vitiligo (Non-segmental Vitiligo):
- Many patches all over the body
- Symmetrical pattern on both sides of the body
- Most common type, also called ‘universal’ or ‘complete’ vitiligo
Is Vitiligo Hereditary?
Yes, vitiligo can be considered hereditary to some extent. While it is not directly linked to family genetics, it can run in families. Here’s what you need to know:
Family History:
- About 30% of people with vitiligo have a family history of the condition.
Inheritance Risk:
- Children of parents with vitiligo have a higher chance of developing it.
- However, having a parent with vitiligo does not guarantee that a child will get it.
Genetic and Environmental Factors:
- Vitiligo likely results from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers.
- Other factors, such as autoimmune responses, might also play a role.
- Early Detection: If you have a family history of vitiligo, early monitoring and consultation with a dermatologist can help manage and mitigate the condition effectively.
What causes vitiligo?
Vitiligo occurs due to the lack of pigment in the skin, which happens because there aren’t enough functioning melanocytes to produce melanin. The exact reason why vitiligo develops is still unknown. However, several factors are believed to contribute to the condition:
- Autoimmune Link:
- Vitiligo is often associated with autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues instead of foreign cells like viruses or bacteria.
- The first signs of vitiligo may appear in areas of the skin that have suffered extensive sun damage.
Autoimmune Conditions Associated with Vitiligo
Approximately 15-25% of people with vitiligo may also have another autoimmune disease. Common autoimmune conditions linked to vitiligo include:
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid gland
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder affecting the joints
- Type 1 Diabetes: A chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to scaling and inflammation
- Pernicious Anemia: A decrease in red blood cells when the body can’t absorb enough vitamin B-12
- Addison’s Disease: A disorder in which the adrenal glands don’t produce enough hormones
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An autoimmune disease that affects the skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs
- Celiac Disease: An immune reaction to eating gluten
- Crohn’s Disease: A type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Ulcerative Colitis: Another type of IBD that causes long-lasting inflammation and sores in the digestive tract
Many people with vitiligo also notice a correlation between eczema and their vitiligo patches.
Vitiligo Triggers
Several factors can contribute to the onset of vitiligo, including:
- Stress
- Skin Damage:
- Critical sunburn
- Cuts or injuries
- Heredity:
- Family history of vitiligo
- Hormonal Changes:
- For example, during adolescence
- Chemical Exposure
- Liver and/or Kidney Issues
Products that contain phenol (also known as carbolic acid or phenic acid) can be possible triggers of vitiligo. These products include:
- Adhesives
- Deodorants
- Disinfectants
- Duplicating paper
- Germicidal detergents
- Insecticides
- Latex gloves
- Paints
- Photographic chemicals
- Printing inks
- Soap antioxidants
- Synthetic oils
- Varnish and lacquer resins
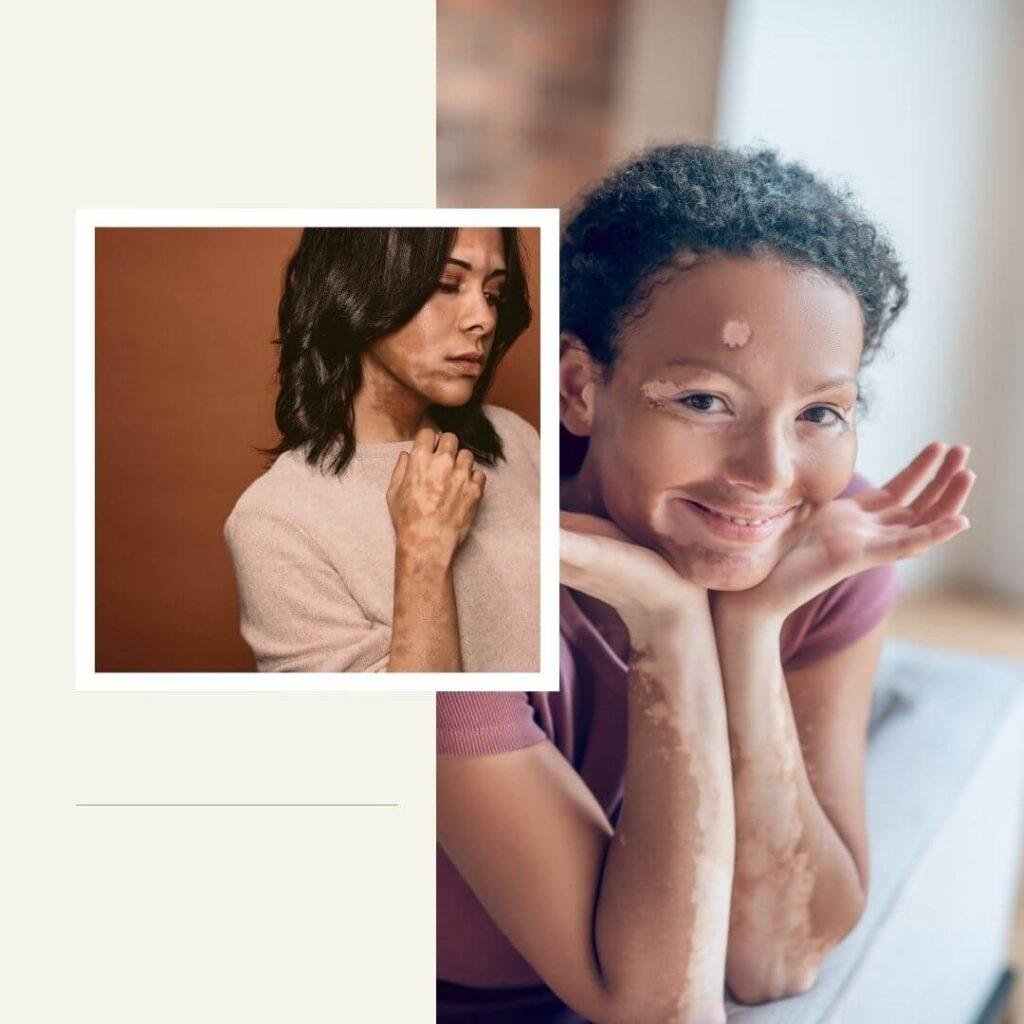
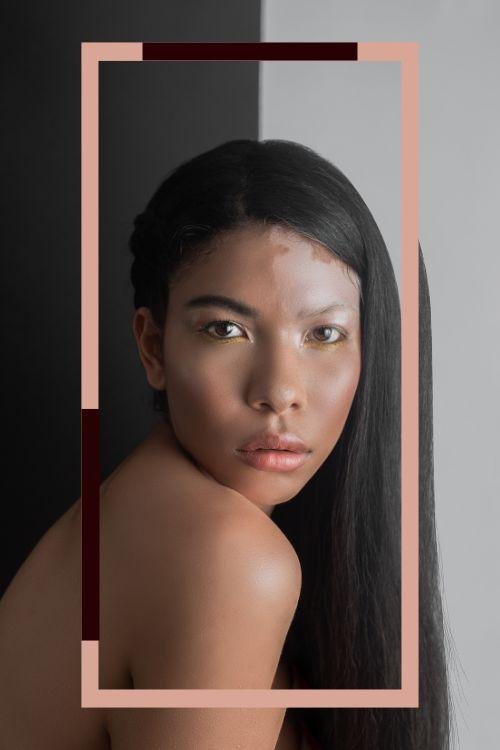


Vitiligo has significant psychological effects, often due to societal perceptions and stigmatization.
Psychological Impact of Vitiligo
Marriage and Social Stigma:
- In conservative families, individuals with vitiligo or their family members are often deemed unfit for marriage.
- Women with vitiligo frequently face discrimination in marriage. Developing vitiligo after marriage can sometimes lead to divorce.
Emotional and Mental Health:
- Social stigmatization can lead to low self-esteem, anxiety, embarrassment, anger, and even serious depression.
- This psychological impact can occur regardless of the extent of the condition, particularly when visible areas like the face and hands are affected.
Vitiligo Treatment Options
Treating vitiligo involves a combination of medications and light-based therapies designed to halt disease progression and promote repigmentation.
Vitiligo Treatment in Thane
Vitiligo treatment involves a range of therapies aimed at halting disease progression and encouraging repigmentation. Here’s a comprehensive look at the available treatments:
Medications
Immune-modifying drugs can help stabilize vitiligo and prevent its spread. Topical creams and lotions are often used to stimulate melanin production and restore pigmentation in affected areas. Consistent, long-term use is crucial for effective results.
Health Supplements
Vitamins and antioxidants play a supportive role by providing essential micronutrients to the skin, which can help slow down disease progression and protect against sun damage.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy using narrow band UVB (311 or 308 excimer wavelength) is highly effective in managing vitiligo. It works by slowing the progression of white patches and stimulating melanin production from hair follicles and surrounding areas. Treatments are typically administered 2-3 times per week and should continue for 1 to 3 months, or longer, for optimal results. Portable devices for home use are also available.
Micro-Needling
Micro-needling with active compounds (collagen pin) can produce redness in the patches and stimulate color from the periphery, helping to spread existing pigment and cover patches more quickly.
Regenerative Treatments
Advanced regenerative treatments like Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy and progenitor cell therapy (active regenera) can accelerate repigmentation. These treatments harvest growth factors from the patient’s own blood or skin and inject them into the patches to stimulate melanin production.
Surgical Options
For more stubborn patches, surgical options such as skin grafting, blister grafting, and cellular suspension transplant can be considered. These procedures involve transplanting healthy skin or melanocytes to the depigmented areas.
Personalized Care
Finding the right vitiligo treatment requires patience and consistency. At our clinic, Dr. Sharmila Patil offers a personalized approach to vitiligo care, ensuring you receive the most effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and start your journey toward effective vitiligo management and repigmentation.
What Our Patients Are Saying
It was a great experience to visit Dr. Sharmila Patil’s clinic as a first timer. The staff was very friendly and helpful and doctor thoroughly explained me the treatment options and answered all my doubts. She is an excellent dermatologist and i recommend everyone with skin and hair issues to seek advise from her. My worries has been solved by her consultation & my problem by her medicines. It’s worth the time and money.

Ravi Nakum
Thane West
She is very kind and helps us to recover from the disease by giving suggestions for day-to-day life with medicines. It was my second time and she treated me same as I experienced before also it’s very helpful to have such doctor’s consultation and their treatments.

Shalini
Thane West
Posted on
Google map
Book Appointment
- Mob: 8469603603
- Tel: 022 2540 5537
- Email: info@drsharmilapatil.in
Nearest Station: Thane West
Nearest Airport: Mumbai Airport
Landmark: Mango Showroom Thane



